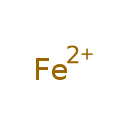
Showing metabocard for Fe2+ (LMDB00218)
| Record Information | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 1.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creation Date | 2016-07-13 19:44:57 UTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 2016-07-20 20:58:13 UTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lmdb | LMDB00218 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Secondary Accession Numbers | None | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolite Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Name | Fe2+ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. Iron makes up 5% of the Earth's crust and is second in abundance to aluminium among the metals and fourth in abundance among the elements. Physiologically, it. exists as an ion in the body. Iron (as Fe2+, ferrous ion) is a necessary trace element used by all known living organisms. Iron-containing enzymes, usually containing heme prosthetic groups, participate in catalysis of oxidation reactions in biology, and in transport of a number of soluble gases. Iron is an essential constituent of hemoglobin, cytochrome, and other components of respiratory enzyme systems. Its chief functions are in the transport of oxygen to tissue (hemoglobin) and in cellular oxidation mechanisms. Inorganic iron involved in redox reactions is also found in the iron-sulfur clusters of many enzymes, such as nitrogenase (involved in the synthesis of ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen) and hydrogenase. A class of non-heme iron proteins is responsible for a wide range of functions such as ribonucleotide reductase (reduces ribose to deoxyribose; DNA biosynthesis) and purple acid phosphatase (hydrolysis of phosphate esters). When the body is fighting a bacterial infection, the body sequesters iron inside of cells (mostly stored in the storage molecule ferritin) so that it cannot be used by bacteria. Depletion of iron stores may result in iron-deficiency anemia. Iron is used to build up the blood in anemia. Humans experience iron toxicity above 20 milligrams of iron for every kilogram of weight, and 60 milligrams per kilogram is a lethal dose. Over-consumption of iron, often the result of children eating large quantities of ferrous sulfate tablets intended for adult consumption, is the most common toxicological cause of death in children under six. The DRI lists the Tolerable Upper Intake Level (UL) for adults as 45 mg/day. For children under fourteen years old the UL is 40 mg/day. Iron is a metal extracted from iron ore, and is almost never found in the free elemental state. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula | Fe | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Weight | 55.845 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 55.934942133 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name | lambda2-iron(2+) ion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Name | lambda2-iron(2+) ion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Registry Number | 15438-31-0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES | [Fe++] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/Fe/q+2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key | CWYNVVGOOAEACU-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of inorganic compounds known as homogeneous transition metal compounds. These are inorganic compounds containing only metal atoms,with the largest atom being a transition metal atom. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Inorganic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Homogeneous metal compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Homogeneous transition metal compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Homogeneous transition metal compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ontology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Status | Detected but not Quantified | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Origin | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biofunction | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Application | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular locations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biofluid Locations and Tissue Locations |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DrugBank ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMDB ID | HMDB0015531 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FooDB ID | FDB030855 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phenol Explorer ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KNApSAcK ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BiGG ID | 33552 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BioCyc ID | FE%2b2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| METLIN ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PDB ID | FE2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikipedia Link | Iron | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemspider ID | 25394 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEBI ID | 29033 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PubChem Compound ID | 27284 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kegg Compound ID | C14818 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YMDB ID | YMDB00379 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ECMDB ID | ECMDB00692 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General References | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||